Eps 1: Why structuring content in XML will never go out of style
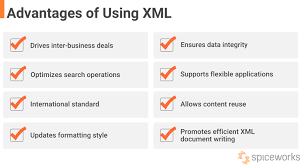
Structuring content in XML remains timeless due to its flexibility and scalability. XML allows separation of content and presentation, facilitating easier updates and consistency across multiple platforms. It supports diverse data types and complex structures, ensuring long-term data integrity and accessibility. XML also enhances data sharing and interoperability between disparate systems, promoting reusability and reducing redundancy. Its human-readable format and strong industry support contribute to its enduring relevance despite the emergence of newer technologies. Consequently, XML’s adaptability and robustness continue to make it a vital tool for content management and data exchange.
| Seed data: | Link 1 |
|---|---|
| Host image: | StyleGAN neural net |
| Content creation: | GPT-3.5, |
Host

Heidi Cook
Podcast Content
Moreover, XML's hierarchical structure naturally lends itself to representing nested data, a common requirement in many modern applications. This makes it incredibly efficient for tasks such as document storage, configuration setups, and data serialization. Its well-defined format ensures that data integrity and consistency are maintained, which is crucial for data validation and transformation processes. The ability to easily transform XML data using XSLT (Extensible Stylesheet Language Transformations) further enhances its versatility, allowing seamless data presentation across multiple platforms without altering the underlying content.
XML's cross-platform and cross-language compatibility is another reason for its enduring relevance. It bridges the gap between diverse systems and technologies, enabling smooth and efficient data interchange. Many industry standards and protocols, from SOAP (Simple Object Access Protocol) in web services to RSS feeds for content syndication, are built on XML. This has established a vast ecosystem of tools and libraries that support XML, ensuring that it continues to be robustly supported and integrated into future technologies.
Additionally, as data continues to grow exponentially, the need for structured and well-organized data becomes even more critical. XML’s schema validation ensures that the data adheres to predefined structures and types, reducing errors and improving data quality. Its backward compatibility and support for namespaces allow for incremental updates and extensions without breaking existing systems, making it a sustainable choice for long-term projects.
In the context of regulatory compliance and legacy systems, XML remains indispensable. Many industries, including finance, healthcare, and government, rely on XML for its ability to maintain and exchange data records accurately and securely. Its adoption in standards such as HL7 in healthcare and ISO 20022 in finance underscores its critical role in meeting rigorous data exchange requirements.
In summary, the enduring relevance of XML lies in its ability to adapt, integrate, and validate data in a way that few other formats can match. Its structured yet flexible nature ensures that as new technologies emerge, XML will continue to provide the foundation needed to maintain data integrity, facilitate interoperability, and ensure long-term viability. The principles of structured, self-descriptive data representation that XML embodies are here to stay, making it a timeless asset in the ever-evolving world of technology.