Eps 1: types of inflation in economy and why
— type of inflation in economy and why
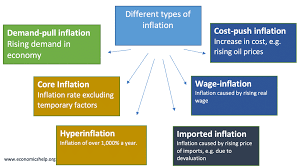
In a 10-minute podcast titled "Types of Inflation in Economy and Why," various types of inflation and their causes are discussed. The podcast starts by explaining that inflation refers to a general increase in prices of goods and services over time. It then goes on to outline three main types of inflation. Firstly, demand-pull inflation is discussed, which occurs when demand for goods and services surpasses the available supply. This type of inflation is commonly observed during periods of economic growth when people have higher incomes and are willing to spend more. It is typically caused by factors like increased consumer spending, government expenditures, or expansionary monetary policy. Secondly, cost-push inflation is explored, which results from increased production costs leading to higher prices for consumers. This type of inflation can be provoked by various factors such as rising wages, increased raw material costs, or high taxes on businesses. When producers face higher costs, they pass them on to consumers through increased prices. Lastly, built-in inflation is discussed, which refers to an essential element of the inflationary process itself. It arises from expectations of future price increases by workers and firms, leading to wage and price adjustments that further fuel inflation. For instance, when workers anticipate higher prices, they demand higher wages, which, in turn, forces businesses to raise prices, solidifying a continuous inflationary cycle. Furthermore, the podcast provides insights into why inflation occurs in an economy. Firstly, it highlights that moderate inflation can be beneficial as it encourages spending, investment, and economic growth. It also mentions how a small amount of inflation is necessary to counter deflation, a dangerous economic condition characterized by falling prices and reduced economic activity. However, excessive inflation can have detrimental effects on the economy, leading to reduced purchasing power, increased economic uncertainty, and environmental consequences. Central banks play a crucial role in combating inflation by implementing monetary policies such as raising interest rates or reducing the money supply. In conclusion, the podcast offers an overview of three major types of inflation: demand-pull inflation, cost-push inflation, and built-in inflation. It also explains the reasons behind inflation and highlights the importance of maintaining a balance to ensure economic stability.
| Seed data: | Link 1 |
|---|---|
| Host image: | StyleGAN neural net |
| Content creation: | GPT-3.5, |
Host

Angel Sims
Podcast Content
Introduction:
Inflation is an essential economic concept that impacts every aspect of an economy. It refers to the sustained increase in the general price level of goods and services over a period of time. Inflation can be caused by various factors and can have several types, each with its own distinct characteristics and effects on the economy. Understanding the different types of inflation is crucial for policymakers, investors, and individuals as it helps in formulating suitable strategies to mitigate its adverse effects. This podcast aims to shed light on the different types of inflation in the economy and explores the reasons behind their occurrence.
1. Demand-Pull Inflation:
Demand-pull inflation occurs when aggregate demand in an economy exceeds the available supply of goods and services. It is primarily caused by increased consumer spending, government spending, or investments. When the demand for products and services rises rapidly, producers tend to increase their prices to match the increased demand. This results in an upward pressure on the general price level, leading to demand-pull inflation.
One of the primary drivers behind demand-pull inflation is strong economic growth. When an economy is booming, consumers tend to have more disposable income, leading to increased spending. Additionally, expansionary fiscal and monetary policies adopted by the government can also contribute to increased demand and subsequent inflation.
2. Cost-Push Inflation:
Unlike demand-pull inflation, cost-push inflation occurs when the cost of production for goods and services increases, leading to a rise in prices. This increase in production costs can be caused by various factors such as a rise in wages, an increase in the price of raw materials, or higher taxes on businesses. When businesses face higher production costs, they tend to pass on the burden to consumers by increasing the prices of their goods and services.
One significant factor contributing to cost-push inflation is rising wages. When workers demand higher wages to offset the rising cost of living, businesses have to increase prices to maintain their profit margins. Another factor is a rise in the price of raw materials, such as oil, which can, in turn, increase the prices of various products, from transportation to manufacturing.
3. Built-In Inflation:
Built-in inflation is the result of past inflationary expectations becoming embedded in the wage and price-setting behavior of individuals and businesses. A key assumption behind built-in inflation is that people's expectations for future inflation impact their current economic decisions. If individuals and businesses expect prices to rise in the future, they will negotiate higher wages and increase prices, perpetuating an inflationary cycle.
Built-in inflation can be driven by multiple factors, such as labor unions bargaining for higher wages based on anticipated inflation, firms providing cost-of-living adjustments to their employees' pay, and businesses raising prices due to anticipated increases in input costs. Though built-in inflation tends to be self-perpetuating, it can be particularly challenging to tackle as it requires a change in expectations and behaviors.
Conclusion:
Inflation is a complex phenomenon, influenced by several factors, and can manifest in various forms. Understanding the different types of inflation is crucial to grasp their underlying causes and address their impacts effectively. Demand-pull inflation, caused by excessive aggregate demand, can be attributed to strong economic growth and expansionary fiscal policies. On the other hand, cost-push inflation, caused by rising production costs, can be linked to factors such as increasing wages and higher raw material prices. Lastly, built-in inflation results from expectations of future inflation becoming embedded in wage and price-setting behaviors.
By analyzing and comprehending the types of inflation and their causes, policymakers can design appropriate monetary and fiscal policies to manage and control their adverse effects. Moreover, businesses and individuals can adjust their strategies and investments to mitigate the impact of inflation on their finances. Ultimately, a prudent understanding of inflation helps in fostering a stable and prosperous economy for all.