Eps 417: the brain
— The too lazy to register an account podcast
| Host image: | StyleGAN neural net |
|---|---|
| Content creation: | GPT-3.5, |
Host

Stacey Wade
Podcast Content
The brain receives information from many sources, often from many at the same time, and interprets this information in a variety of ways, including visual, auditory, tactile and tactile.
She receives these messages, often from many people at the same time, and interprets them in many ways. It controls the brain, regulates the heart and respiratory rate, and also determines how people respond to stimuli such as sound, light, touch, smell, sound, and touch.
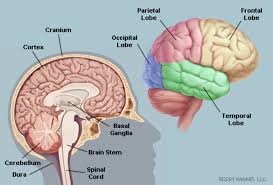
The brain is an organized structure that is divided into many components that perform specific and important functions. It is a complex organ in the skull that controls activity via the nervous system. The largest and most famous part of the brain are the frontal lobes or frontal lobes and temples. Part of this is the central nervous system , which is responsible for processing sensory information such as sound, light, touch, smell, sound and touch.
The brain stem is located in the upper anterior part of the cranial cavity and is connected to the spinal cord. It consists of a medulla oblongata, a pon and a midbrain. The main functions of this brain include the transmission of information between brain and body, the supply of cranial nerves to the face and head, and the execution of important functions such as the control of the heart, breathing and consciousness. The spinal nerve, central nervous system and other nervous systems are present in all vertebrae.
The thalamus transmits sensory and motor signals to the cerebral cortex and is involved in regulating consciousness, sleep and alertness. It is circled by the cerebral cortex, the central nervous system and other parts of the brain such as the amygdala.
The hypothalamus connects the nervous system with the endocrine system, where hormones are produced. The brain is responsible for the production of hormones such as testosterone, cortisol, adrenal glands and cortisol.
The brain is located in the skull, encased in three layers of sheets called meningings, which help protect it from the outside world such as sun, wind, rain, cold, heat and cold air.
This fluid helps to protect and cushion the brain when shaking or nodding, for example, and even fills the space between the brain and the brain. This fluid also helps to get oxygen into your brain so it can function and helps it send messages to the body. The brain stem, which is connected to it by the spinal cord, stores oxygen and nutrients. Although it is one of the most basic parts of our brain, it is also responsible for the survival of our body and controls many other important functions such as breathing, heart rate, blood pressure and blood flow.
The brain stem is a tubular mass of fluid 8 cm long, which becomes more complex as the spinal cord grows and brain cells develop in the brain and other parts of the body.
The midbrain, also called mesencephalon, is the part of the brain stem that connects the posterior brain with the forebrain and the cerebral cortex. The last part of our brain is our forebrain, which contains the thalamus , the amygdala and the neocortex, among other structures, as shown in Figure 1. In addition to its role as the primary control centre of the central nervous system, it also helps to control the vital functions of the body.
The cerebrum of the brain consists of a corpus callosum that connects the right and left hemispheres. The hypothalamus, located to our right, and the thalamus play a key role in regulating the body - regulating processes such as breathing, heart rate, blood pressure, and oxygen levels in the blood. Our brain is responsible for regulating many aspects of our body, from breathing control to fighting flight and other bodily functions.
The functions of the cerebrum include decisions - decision-making, problem solving, reasoning, and other cognitive functions. The brain controls many aspects of our body, such as breathing, heart rate, blood pressure, oxygen content, body temperature, breathing and breathing.
The left hemisphere controls the right hemisphere of the body, and there are two types of brain regions: the cerebral and frontal lobes. The right side or brain controls our left side and body; the left side - the brain - controls our right parts such as our eyes, ears, nose, mouth, throat and eyes.