Eps 645: Postgres query tuning
— The too lazy to register an account podcast
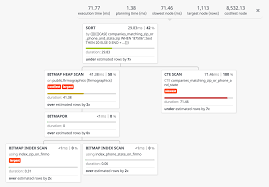
If your application uses many functions, auto_explain is invaluable for getting detailed execution plans.
You should run queries at least 3 times and average the results to compare apples to apples.
Make sure your table statistics are accurate by reviewing your vacuuming strategy
Host

Stacey Pena
Podcast Content
Query memory simplifies debugging by helping you quickly find out which queries are running at the slowest response times and which are running faster. In some cases, the query is written too fast, causing a slow response time, while in others it is too slow.
It is important to be able to analyze how the query is executed and to find out why it is inefficient. One way to optimize queries is to review your query plan to see how your queries are executed, and customize them to be more efficient. The plan of a query may provide you with the best way to launch queries, but it is important that you are aware of how queries are executed and how they can be best executed.
EXPLAIN shows you the query plan for SQL queries in Postgres, and you will see how you can use a hidden function of PostgreSQL to be tagged in your Postgres database, SQL query tuning. You can improve performance by taking jobs from the cte and filtering through it, rather than waiting for queries to join other tables.
This service has experienced tremendous growth and we have had many customers turn to us to achieve optimal query performance.
While MySQL is focused on fast performance for web-based applications, PostgreSQL provides the general features of a traditional database application. While quality, consistency and query optimization have their place in a modern database, the quality and consistency of query optimization have no place. The Postgres Explain Viewer is a tool to simplify reading the query plan and visualize the problem.
Query is the best way to find out if your database is running 24x7 and wikiHow teaches you how to use the SQL Server Query Store to monitor the performance of database queries. When multiple users send requests to the database server, it is forwarded to each of them in real time.
The most efficient path to execute queries is created by creating a list of the most common execution paths for each user in the database server.
This is a rather arcane rule that affects performance, but it makes it easier for PostgreSQL developers to maintain it. Since two API's are already integrated into the query layer of the framework , it seems easy and natural to improve the query performance of analytics. Besides improving the performance of long running analytical queries, postgreSQL 11.0 has been extended with a number of new features.
The query logger is activated to see which queries are most common, and then EXPLAIN _ ANALYZE is used to determine the query cost.
The ability to choose from many different types of indices is a power that must also be used carefully. These PostgreSQL query optimization tips help you speed up queries in a multi-GB database by 10-100 times. Date filter, which is the most common query type in the Postgres database and the second most popular in MySQL.
However, this does not mean that you should not compare your requests twice with real case scenarios, which I will explain below.
The most important thing is that the EXPLAIN command helps you understand which specific index is used and how. I strongly recommend using it for analysis, as there are many cases where there are higher query costs, but the time that you run is actually shorter. The difference is that it displays the cost based on the statistics collected from the database, but actually performs an "explanation" to show you the processing time at each stage.
The ability to see the indexes is one of the most important aspects of postgres query tuning that I # I found out about it. Hopefully this will give you a good idea of how to tailor your PostgreSQL database to performance.
You should be able to optimize your database configuration to match what you use to make the most of it. By now, you should be ready to analyze your queries , draw logs for further insight, and modify your indices for faster performance.
If the percentile is below the value of the input, use percentile _ cont to get an interpolated result. This is just one example of how postgresql query tuning works. Be patient and look for more information about the PostgresQL system to get the best performance results in the future.
This allows you to profile your application's SQL queries and see exactly how PostgreSQL Scheduler will handle them. You can then use this information to improve your PostgresQL query performance. This book will also benefit the internal architects of PostSQL, as there is a lot of information about monitoring performance using benchmarking tools.