Eps 1: how attributes in programming are used to store data
— attributes are often used to store data in python
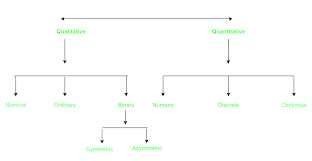
Attributes in programming are variables or properties associated with objects that store data. They help define the characteristics of an object and can hold different types of data, such as numbers, strings, or even other objects. By using attributes, programmers can encapsulate data within objects and provide a structured way to access and modify this information through methods. Attributes support the principles of object-oriented programming by enabling data encapsulation and abstraction, thus allowing for the creation of more modular and maintainable code.
| Seed data: | Link 1 |
|---|---|
| Host image: | StyleGAN neural net |
| Content creation: | GPT-3.5, |
Host

Allan Gregory
Podcast Content
Furthermore, attributes are instrumental in maintaining the integrity and consistency of the data. By employing access modifiers such as private or protected attributes, encapsulation is achieved, ensuring that data is accessed and modified only through defined methods. This not only upholds the principle of data hiding but also prevents unintended interference and maintains control over how attributes are manipulated. Encapsulation enables developers to create methods—setters and getters—that validate the data being assigned to attributes, thereby enforcing constraints and rules within the class.
Attributes also play a critical role in inheritance, where subclasses inherit attributes from their parent classes, promoting code reuse and enhancing productivity. The inherited attributes allow subclasses to possess default properties and behaviors while also providing the flexibility to introduce or override attributes tailored to the unique needs of the subclass. This hierarchical organization not only simplifies the code but also fosters a modular design, making it easier to manage and extend over time.
In addition to attributes being static and defined at the class level, dynamic attributes can be added at runtime, expanding the flexibility available in certain programming languages. This allows objects to adapt to additional data requirements as needed without altering the underlying class structure. Dynamic attributes enable developers to extend objects with new properties in response to evolving application needs, enhancing the capacity to handle diverse datasets and complex scenarios.
In data-driven applications, attributes serve as key units for data representation and are immensely valuable in data serialization and deserialization processes. They facilitate the conversion of object data into formats like JSON or XML, which can be transmitted or stored and subsequently reconstructed back into objects. This capability is paramount for interoperability between different systems and for persisting the state of objects across different layers of an application or during different execution intervals.
Finally, the use of attributes in configuration and metadata purposes cannot be overlooked. Attributes can carry metadata about the class or object, such as validation rules, database mapping details, or API endpoint information. This metadata guides how objects are processed, validated, or persisted, enhancing the automation and efficiency of various operations within an application. By leveraging attributes, developers can significantly streamline configuration management and ensure consistency across the application lifecycle.
In conclusion, attributes in programming are vital for data storage, encapsulation, inheritance, dynamic flexibility, data serialization, and metadata management. They offer a robust mechanism for defining, accessing, and maintaining the state of objects. Attributes not only contribute to the structured and efficient design of software systems but also empower developers to harness the full potential of object-oriented programming paradigms. As a result, they play an indispensable role in the creation of scalable, maintainable, and high-quality software solutions.