Eps 1: Bert For Sequence Classification class from the Transformers
— test
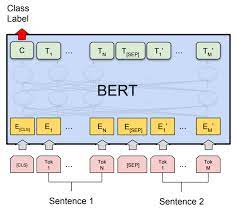
In the podcast titled "Bert For Sequence Classification class from the Transformers," the speaker discusses the use of Bert, a popular natural language processing model, for sequence classification tasks. Bert, short for Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers, has proven to be highly effective in various NLP tasks due to its ability to understand context and capture nuanced relationships between words. The speaker explains that in order to use Bert for sequence classification, we need to fine-tune the pre-trained model. Fine-tuning involves taking the base Bert model and training it on a specific task, such as sentiment analysis or text categorization. By fine-tuning, we can leverage the pre-trained model's knowledge and adapt it to our specific sequence classification task. The speaker highlights the importance of using the right input representation for sequence classification. For example, when classifying a sentence for sentiment analysis, we can use the [CLS] token provided by Bert as the representation of the whole sentence. Additionally, the speaker mentions the significance of attention masks and token type IDs in the input representation for accurate sequence classification. Furthermore, the podcast delves into the implementation details of using Bert for sequence classification using the PyTorch library. The speaker provides a step-by-step guide on preprocessing the data, loading and fine-tuning the Bert model, and evaluating the performance of the trained model. Overall, the podcast emphasizes the effectiveness of using Bert for sequence classification tasks by fine-tuning the pre-trained model. It also offers insights into the implementation process using PyTorch, providing a valuable resource for individuals interested in utilizing Bert for sequence classification.
| Seed data: | Link 1 |
|---|---|
| Host image: | StyleGAN neural net |
| Content creation: | GPT-3.5, |
Host

Rhonda Romero
Podcast Content
In recent years, Natural Language Processing (NLP) has witnessed significant advancements that have revolutionized the way we interact with computers. One of the key breakthroughs in NLP has been the development of transformer-based models, which have set new standards in tasks such as sequence classification. Among these transformer models, BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers) has emerged as a powerful tool that has yielded remarkable results across various NLP tasks. In this podcast, we will delve into the specifics of the BERT for Sequence Classification class from the Transformers library and explore how it has transformed the field of NLP.
To start, let's understand what sequence classification entails. Sequence classification refers to the task of assigning a predefined label to a given input sequence. This could range from categorizing tweets as positive or negative sentiment, to classifying news articles as fake or real. One of the key challenges in sequence classification is capturing the contextual information present in the input sequence. Traditional methods often struggle with this due to their inability to understand the semantic relationships between words and the context in which they are used.
This is where BERT comes into play. BERT is a pre-trained transformer model that captures the contextual understanding of words by considering both their left and right contexts. This bidirectional approach allows BERT to capture a deeper understanding of the context and meaning of the words used in a given sequence. Unlike traditional language models, BERT does not rely solely on fixed-length context windows but takes into account the entire input sequence. This results in better contextual representations and enhances the accuracy of sequence classification tasks.
Now, let's dive into the BERT for Sequence Classification class itself. The Transformers library provides a straightforward and efficient way to leverage BERT for sequence classification tasks. The BERT for Sequence Classification class encapsulates the functionalities required to use BERT as a sequence classifier without having to write extensive code from scratch. This class provides a high-level API that enables researchers and developers to quickly integrate BERT into their projects and leverage its powerful capabilities.
One of the key features of the BERT for Sequence Classification class is its ability to handle variable-length sequences. BERT can handle sequences of different lengths without the need for padding or truncating the input. This is achieved through the use of the attention mechanism in transformers that allows BERT to attend to relevant parts of the input sequence while disregarding unnecessary information. This flexibility makes BERT a versatile tool for sequence classification, where the length of the input may vary greatly.
Another crucial aspect of the BERT for Sequence Classification class is its support for fine-tuning. After pre-training BERT on a large corpus of text, the model can be fine-tuned on a specific task, such as sentiment analysis or document classification. Fine-tuning BERT involves training the model on a smaller dataset tailored to the specific task at hand. This allows BERT to refine its understanding of the given task and adapt its parameters to achieve optimal performance. The fine-tuning process significantly improves the accuracy and effectiveness of BERT for sequence classification tasks.
The BERT for Sequence Classification class also offers several hyperparameters that can be tuned to optimize the performance of the model. These hyperparameters include the number of layers, the attention mechanism parameters, and the learning rate. By experimenting with different combinations of hyperparameters, researchers and developers can fine-tune BERT to achieve the best results for their specific sequence classification task.
In conclusion, the BERT for Sequence Classification class from the Transformers library has transformed the field of NLP by providing an efficient and powerful tool for sequence classification tasks. With its ability to capture contextual information, handle variable-length sequences, and support fine-tuning, BERT has significantly improved the accuracy and effectiveness of sequence classification models. As the field of NLP continues to evolve, BERT and similar transformer-based models are expected to play a key role in advancing the capabilities of computers in understanding and processing human language.